What’s What of Uterine Fibroid Embolization: Understanding Every Component of UFE
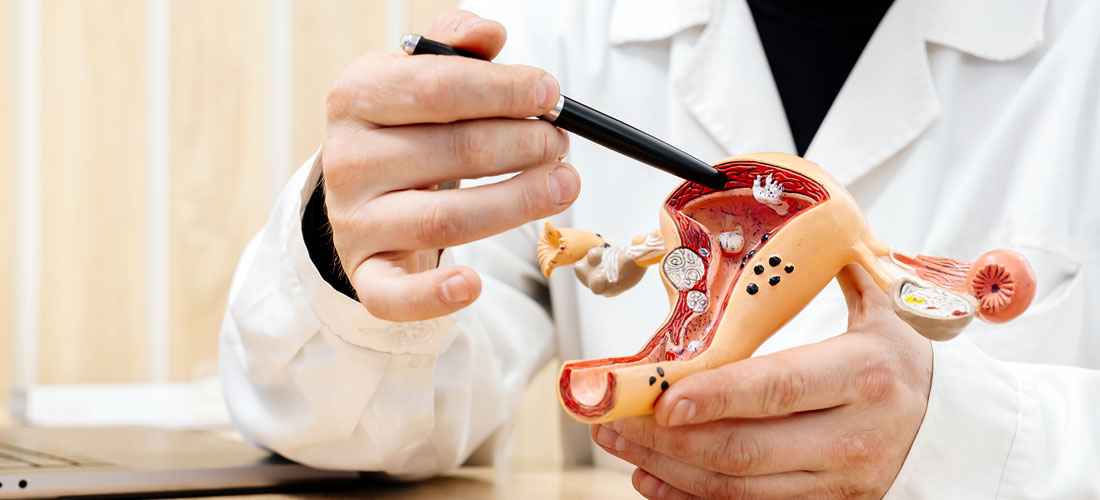
Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE) is one of the most advanced, uterus-preserving treatments available for symptomatic fibroids. Many patients understand how UFE is performed: the broad idea of blocking blood supply to shrink fibroids; the true success of UFE depends on several interconnected pieces: the biology of fibroids, imaging science, micro-devices, precision techniques, and post-procedure recovery.
Understanding these components helps patients appreciate why UFE is both effective and precise, and why outcomes depend heavily on imaging quality, embolic materials, and technical experience.
The blog below is a clear, detailed breakdown of each element involved in Uterine Fibroid Embolization procedure—from the structure of fibroids to the devices, materials, and biological responses that shape results.
Fibroids: What They Really Are
The biology
Fibroids, or leiomyomas, are benign, smooth-muscle tumours of the uterus.. Fibroids are made of dense bundles of muscle fibres mixed with connective tissue. They are not cancerous, but they can distort the uterus and its blood supply. They require a rich blood supply from branches of the uterine arteries to grow and remain symptomatic.
Why blood supply matters
Fibroids are hypervascular, meaning they draw more blood than normal uterine tissue. This dense vascular network is the reason embolization works so reliably.
An MRI helps determine:
- how intensely a fibroid enhances
- whether it has necrotic areas
- whether it receives blood from uterine or ovarian arteries
Knowing vascular behaviour influences how well fibroids shrink after UFE.
Types of fibroids and their different behaviour
Fibroid behaviour depends on their location:
- Intramural: Grows within the muscular wall, causes bulk symptoms and bleeding
- Submucosal: Grows beneath the uterine lining, distorts the cavity, causes heavy bleeding
- Subserosal: Grows on the outer surface of the uterus, causes pressure symptoms
- Pedunculated: Attached by a stalk, can cause intermittent or positional pain
Recurrence
When treated with UFE, true recurrence of treated fibroids is low. Most “recurrence” after UFE refers to new fibroids forming, usually in women who are younger or have diffuse fibroid disease. Careful imaging and selective embolization reduce this likelihood.
What Do Uterine Arteries Do?
The uterine arteries arise from the internal iliac arteries and supply blood to:
- The uterus
- Fibroids
- Part of the cervix
Fibroids often “steal” blood flow, forming enlarged, tortuous vessels feeding their growth.
UFE targets only these branches. Normal uterine tissue continues to receive blood from collateral circulation.
Understanding this anatomy is essential for safe catheter positioning and complete fibroid treatment.
What Is Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE)?
Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE) is a minimally invasive procedure that blocks the fibroid’s blood supply, causing it to shrink. It is done by an interventional radiologist through a tiny puncture in the wrist or groin.
UFE does not remove the fibroid physically. Instead, it induces controlled infarction that leads to gradual shrinkage. This is one of the key benefits of UFE treatment.
Breaking Down Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE) Components
What is a Catheter?
A catheter is a long, thin, flexible tube used to navigate blood vessels under imaging guidance. They are just a few millimetres wide. They are threaded from the wrist or groin into the uterine arteries during UFE.
Different types serve different purposes:
- Guiding Catheter: Inserted at the entry point and steered into the internal iliac artery. It stabilises access and allows the next catheter to move deeper.
- Microcatheters: A much thinner, highly flexible tube used to reach the tiny branches supplying fibroids. It can navigate sharp angles and very small vessels without damaging the artery.
- Shaped catheters: Designed for challenging anatomy
Why microcatheters matter:
They enable selective embolization, meaning only the fibroid-feeding arteries are treated while protecting healthy uterine tissue. Microcatheters are critical for:
- precise placement
- avoiding non-target embolization
- delivering embolic particles exactly where needed
The quality of the catheter affects safety, speed, and accuracy.
What Are Embolic Particles?
Embolic particles are tiny, calibrated microspheres used to block the blood supply to fibroids. The particles are biocompatible. They are the core component of UFE.
What they are made of
Common materials include:
- Non-resorbable tris-acryl microspheres
- PVA particles (less commonly now in high-end centres)
Embolic particles are not absorbed by the body and are designed to stay in place permanently
Why Permanent Particles?
Fibroids rely on continuous high blood flow. Temporary agents would allow regrowth.
Once the particles block their arteries:
- The fibroid becomes ischemic.
- Tissue gradually shrinks.
- Symptoms like bleeding and pressure reduce over months.
Particle size
Particles come in specific size ranges (usually 500–900 microns). The size is chosen based on fibroid vascularity and patient-specific factors.
Size selection depends on:
- vessel calibre
- fibroid vascularity
- need for deep vs surface-level penetration
Choosing the correct size ensures:
- complete infarction of fibroid tissue
- safety of surrounding structures
- predictable shrinkage
Infarction: What Happens Inside the Fibroid After UFE
Infarction refers to the deliberate loss of blood supply to the fibroid. When its arterial flow is blocked, the fibroid is deprived of oxygen and nutrients, leading to gradual shrinkage. This is a controlled, targeted, and predictable process.
What Happens After Embolization?
- Fibroid cells lose blood flow and soften
- Degeneration begins within hours
- Shrinkage progresses over 3–6 months
- Symptoms improve gradually
- Relief from bulk symptoms as size decreases
What Happens to Fibroids After They Shrink?
Shrinkage reduces:
- Bleeding volume
- Pressure on bladder and bowel
- Pelvic heaviness
- Backache
- Abdominal distention
A good procedure aims for >90% infarction of the dominant fibroid. Typical shrinkage is 30–60%, but symptoms improve far more because pressure is relieved and bleeding reduces. Fibroids do not disappear entirely but become smaller, softer, and less vascular. Some degenerate into scar-like tissue that causes no symptoms.
The uterus itself survives without damage because it has rich collateral blood supply from other pelvic vessels.
What Is Image Guidance?
Accurate imaging is central to safe and effective UFE, beginning well before the procedure itself.
The evaluation and the procedure both depend on different forms of image guidance, each with a specific purpose.
MRI
MRI is the most reliable way to understand the true behaviour of fibroids. It provides clarity on:
- the number and size of fibroids
- their vascularity and growth pattern
- any degeneration within the fibroid
- arterial supply
- whether adenomyosis is also present
An MRI-based assessment ensures that only patients who are likely to benefit undergo UFE, reducing the chances of incomplete results or avoidable re-interventions. This selective approach is what sets apart the best Uterine Fibroid Embolization doctors in Hyderabad from the merely-good ones.
Advanced Cath-lab Technology
During the procedure, image guidance refers to the real-time imaging system that helps the doctor navigate the catheter and deliver particles precisely to the fibroid-feeding vessels. The robotic table movement, ultra-low dose fluoroscopy, fine vessel visualization, and high-precision 3D road-mapping. These improve accuracy while reducing radiation.
Modern interventional suites use high-performance platforms that offer:
- high-resolution views of blood vessels
- wide field coverage without frequent repositioning
- flexible C-arm angulation for optimal working angles
- AI-based optimisation for clearer images with less noise
- lower radiation exposure for patients
- sharper visualisation during catheter movement
These capabilities allow the interventional radiologist to:
- identify all branches supplying the fibroid
- detect collateral vessels that may need treatment
- avoid non-target areas
- perform the procedure with higher accuracy and efficiency
The GE Allia IGS 7 Advantage
Centres equipped with the GE Allia IGS 7 system gain access to several advanced features that directly improve the quality of UFE:
- Fixed, laser-guided gantry positioning for optimal access and stable imaging
- Offset C-arm design, allowing comfortable positioning without compromising imaging angles
- High-resolution flat-panel detector for detailed visualization of small pelvic vessels
- 3D cone-beam CT and 3D road-mapping, which help confirm catheter position and ensure complete coverage of fibroid-feeding arteries
- Dose-efficient imaging chain, enabling lower radiation without sacrificing clarity
- AI-supported image processing, providing cleaner, sharper images during catheter manipulation
These innovations streamline the procedure, improve accuracy, and support safer navigation through complex pelvic vasculature.
Not all hospitals have access to this level of technology, even if UFE is listed as an available service. Centres equipped with advanced image-guided systems can offer safer procedures, better targeting, and more consistent outcomes.
Selective Embolization vs Non-Target Embolization: What Determines Success
Selective embolization means treating the fibroid vessels without compromising:
- normal uterine tissue
- ovarian circulation
- adjacent pelvic organs
Non-target embolization occurs when particles travel to unintended tissues. Avoiding non-target embolization is essential for preserving normal uterine tissue and avoiding complications. Advanced microcatheter design and high-quality imaging reduce this risk by ensuring particles reach only the fibroid vessels.
Experienced specialists use:
- microcatheters
- patient-specific vascular mapping
- live flow analysis
- targeted dosing
This approach results in better symptom relief, faster, better recovery after treatment, and lower complication rates.
What Is the Post-Embolization Inflammatory Response?
After treatment, fibroids undergo controlled degeneration.
This can cause:
- Cramping
- Low-grade fever
- Fatigue
- Pelvic discomfort
This response usually peaks in the first 24 hours and improves rapidly with structured pain pathways.
It is not a sign of complication but is part of the treatment effect.
What Medications Are Used During and After UFE?
During UFE:
- Mild sedation
- Local anesthesia
- Intra-arterial medications to prevent vessel spasm
After UFE:
- NSAIDs to control inflammation
- Antiemetics for nausea
- Short-course antibiotics in specific protocols
- Hydration guidance to reduce discomfort
Pain management is a critical component. Centres with optimised pain pathways dramatically improve patient comfort. UFE can cause temporary cramping due to fibroid ischemia. Modern centres use:
- patient-controlled analgesia
- NSAIDs and anti-spasmodics
- targeted nerve blocks
- early mobilization protocol
With structured care, pain is manageable and short-lived.
Why Is Follow-Up Imaging Needed?
MRI or ultrasound at 3 months and 6–12 months helps confirm:
- degree of shrinkage
- completeness of infarction
- improvement in uterine size
- absence of new vascular supply
Regular follow-up also ensures any rare complications are identified early.
Uterus Preservation & Ovarian Reserve
Impact on uterus
UFE is designed to preserve the uterus structurally and functionally while resolving symptoms.
Ovarian reserve
Most women maintain ovarian function because:
- selective embolization protects ovarian branches
- modern microcatheters improve precision
- risk is highest only in women >45
Younger women generally retain normal hormonal cycles after UFE.
Complexity: Why Experience Matters
Uterine Fibroid Embolization is simple in concept but technically demanding due to:
- variations in pelvic vascular anatomy
- small vessel diameters
- the need for bilateral treatment
- real-time dose management
- precise particle delivery
- careful avoidance of non-target embolization
The strongest results come from centres performing large numbers of embolization procedures with robust imaging and skilled interventional radiologists.
Why Choose RIVEA for Uterine Fibroid Embolization
A successful UFE depends on more than the embolization step alone. It requires a centre that understands every component of the treatment pathway, including fibroid biology, pelvic vascular anatomy, selective catheter techniques, embolic material behaviour, image-guided precision, and the body’s healing response. RIVEA is built around this comprehensive approach.
Interventional Radiology at RIVEA is led by Dr. Arjun Reddy, one of the leading interventional radiologists in South India. He is known for his expertise in complex embolization procedures and for performing UFE with a high degree of accuracy and safety. His experience plays a major role in ensuring both effectiveness and uterine preservation.
RIVEA also invests in state-of-the-art imaging, allowing precise catheter navigation, clearer visualization of fibroid-feeding vessels, and lower radiation exposure. This level of technology supports targeted embolization while protecting surrounding structures.
Structured care, dedicated pain management pathways, and a defined follow-up protocol further strengthen outcomes. Patients receive guidance that covers preparation, recovery expectations, return-to-activity timelines, and long-term monitoring of symptom improvement.
This commitment to high-quality, ethical, and outcome-driven care is reflected in RIVEA’s recent national recognition as one of India’s top emerging specialty care hospitals, highlighting its consistency in delivering safe, evidence-based treatment.
When these elements—expertise, technology, careful selection, and thorough follow-up—come together, UFE becomes a reliable, uterus-preserving solution for women seeking long-term relief from fibroids.
Click here to learn more about:
Uterine Fibroid Embolization
For any inquiries, post your query here:
Ask Rivea
Contact us today to explore your options.
Call Now